In harsh automotive environments, various power field effect transistors (power FETs) are consistently considered to withstand extreme temperature variations and thermo-mechanical stresses. Intermittent short circuits, cold operating conditions, high voltage arcs or noisy short circuits, together with inductive loads and multiple short circuits, can cause the device to become weak, causing it to enter an open, short or resistive mode.
Although power FETs are becoming increasingly robust, they can easily and very quickly fail if they exceed the rated limits. If the transient voltage contains more energy than the rated avalanche breakdown energy level, the device will be damaged and create a destructive thermal event that may eventually cause the device to smoke, ignite or desolder.
RTP devices help provide secondary protection in demanding environments
A new surface mount component, a reflowable thermal protection (RTP) device helps prevent thermal damage from faulty power electronics. This device helps prevent damage caused by unexpected high temperature resistive shorts caused by I2R heating characteristics, as well as hard short circuit overcurrent conditions. The device can be mounted using standard lead-free reflow soldering processes and can replace a variety of redundant power FETs, relays, and a large number of thermal sensors commonly used in automotive and industrial electronics designs.
When a power component fails or a board defect creates an unsafe overtemperature condition, the RTP device is at 200 ° C (a value above the normal operating temperature range, but lower than the melting point of the lead-free solder) The temperature) is disconnected and will interrupt the current, helping to prevent thermal runaway conditions that could lead to fatal damage.
As shown in Figure 1, when the RTP device is placed in series on a power line near the FET, it tracks the FET temperature and disconnects the circuit before a slow thermal runaway condition creates an unexpected overheat condition on the board.
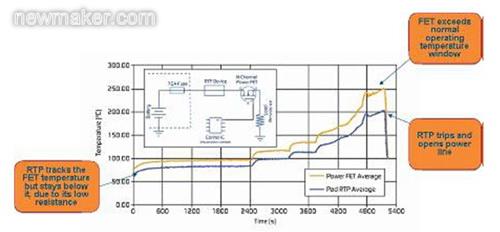
Figure 1. In a chronic thermal runaway situation, the RTP device tracks the power FET temperature until it breaks the circuit at 200 °C.
Protect the cooling fan module from damage caused by thermal runaway
Various Cooling Fan Modules (CFM) are essential for automotive HVAC and engine cooling systems to help cool the engine and prevent potential overheating under special conditions, such as hot weather and slope driving. CFM modules are usually placed under the hood and they experience more extreme temperature changes than those found in the passenger compartment. This thermal stress accelerates the fatigue of the power FET and causes early failure. Components under the hood of the car may also be exposed to "fluid attack," resulting in corrosion and localized hot spots on the printed circuit board.
Normally, the CFM module does not include a microcontroller that can be used for on-board diagnostics and automatically triggers a power FET disconnect signal under certain conditions. Therefore, it is unusable to prevent power FET failure by software methods, so secondary circuit protection becomes necessary, so that thermal runaway does not cause dangerous thermal events.
In some design configurations, the power FET may be directly connected to the battery. In this case, the power supply continues to power the device even if the igniter is turned off. If there is a fault that causes an unsafe temperature, the power from the engine will not interrupt the loop, and the result is a thermal event.
In most automotive cooling fan applications, power FETs are used in the control module to switch the power to the fan motor as needed. There are two typical motor configurations in CFM applications: brush and brushless. Figures 2 and 3 depict two configurations and associated electronics, respectively, and define sensitive areas where unsafe thermal runaway can occur due to power component failure. In these applications, RTP devices help prevent damaging thermal events caused by thermal runaway. The RTP device is placed in a sensitive area of ​​the application and will break the circuit once the temperature exceeds its turn-off temperature.
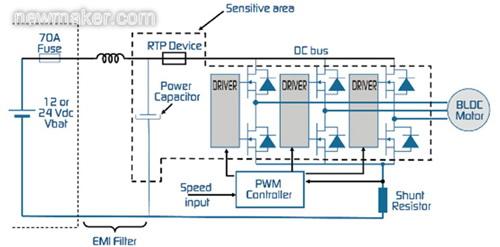
Figure 2. Three-phase brushless DC motor configuration
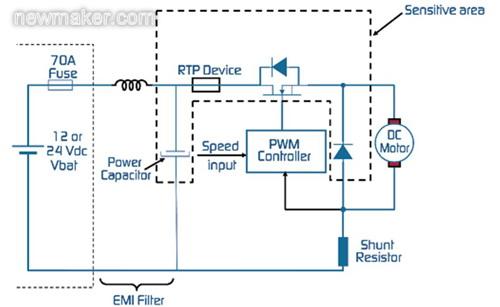
Figure 3. Brush DC motor configuration
to sum up
RTP devices help automotive power electronics systems meet reliability requirements, including cooling fan applications, including ABS, power steering, and PTC heaters. Although this article focuses on power FETs, RTP devices can also help protect against damage from thermal runaway when other components fail, such as capacitors, chips, resistors, and other power components. Thermal runaway caused by failure, or any form of corrosion, causes heat. (end)

Concerned about surprises
Tags: thermal runaway car hood cooling fan thermal event RTP
Previous: Fatigue strength analysis of the telescopic frame of the subway car Next: Common faults and solutions for the lamp-pumped laser marking machine
PP Woven Bag also named Woven Cloth, We professional produce PP bag with 100% virgin polypropylene material,high strength.
PP woven bag are extensively used in the construction of irrigation works, roads, railways, ports, mines, buildings, and more. Having the functions of filtering, draining, isolation and anti-seepage.
Our Plastic Woven Bag export to Malaysia,Singapore,Latvia,American,,Chile,Argentina etc countries.
PP Woven Bag
PP Woven Bag,White PP Woven Bag,PP Woven Fabric,PP Woven Sand Bag
HEBEI TUOHUA METAL PRODUCTS CO.,LTD , http://www.penetting.com