1. Screening and drying of chips
The wood chips are sent to the vibrating screen by the bucket elevator, and the 6-40 mesh wood chips are selected and sent to the cyclone separator by the air blower. The separated wood chips fall into the silo. Then, the airflow is dried, and the wood chips are continuously dropped into the spiral feeder by the disc feeder under the silo, and the hot air duct is added, and the hot air from the hot air furnace is taken away and dried by the high-speed air, and the moisture content of the wood chips is 40. The % drops to 15%-20%, and the dry wood chips fall into the dry sawdust silo after the cyclone separator is separated.
2. Preparation of zinc solution
The zinc chloride solution is prepared according to the requirements of the production, and a zinc chloride solution of a predetermined concentration is prepared. During the preparation, the concentration of 40 US cents of zinc recovered in the recovery process is pumped into the zinc bath, and then fixed zinc chloride and hydrochloric acid are added to prepare a zinc chloride solution of the specified concentration and pH, or directly prepared with water. Alternatively, then pump it into the concentrated zinc bath for use.
3. pinch and
Pump the zinc chloride solution of the concentrated zinc pool into the high-concentration tank of the concentrated zinc solution. Since the wood chips under the wood chip silo are lifted to the metering tank by the bucket elevator, a certain amount of wood chips is put into the kneading machine, and the high level is from the high position. After mixing the concentrated zinc solution in the tank, it is poured into the hopper of the rotary kiln.
4. Activation
The wood chips are added to the rotary kiln by the disc feeder and the screw feeder at the lower part of the hopper, and the hot flue gas is introduced from the other end of the furnace to carbonize and activate the wood chips, and the activated material falls into the discharge chamber and is periodically taken out, using the trolley. Push to the bucket elevator feeding point in the recycling process.
5. Recycling, rinsing
Start the bucket elevator and add the activated material to the recovery tank to recover zinc chloride. First wash with 25-30 Baumezinc zinc chloride solution, the concentrated zinc solution is sent to prepare zinc chloride solution, then washed with dilute zinc solution, add appropriate amount of hydrochloric acid during washing, and heat the solution to 70 degrees Celsius In the above, zinc oxide is converted into zinc chloride. Finally, the concentration of the washing liquid is required to be below 1 Baume. The recovered charcoal is flushed into the rinsing tank with water, rinsed with hot water of 90 degrees Celsius or higher, and an appropriate amount of hydrochloric acid is added during the second rinsing, and heated to boiling to remove iron from the charcoal until the washing liquid contains no iron.
6. Centrifugal dehydration, drying and grinding
The activated carbon is dehydrated in a centrifuge and then dried in an external thermal rotary dryer to a moisture content of 4 to 6%, which is then sent to a ball mill for grinding.
In addition, a special exhaust gas and wastewater treatment system is attached to recover zinc chloride and hydrochloric acid in the flue gas to eliminate pollution.
Requirements for raw materials for zinc chloride activation
The raw material for producing powdered activated carbon by zinc chloride method is mainly wood chips. When producing carbon for sugar, it is better to use chopped wood chips and pine wood chips, and pure fir chips are better. Fresh pine chips contain more turpentine, which is not conducive to the infiltration of zinc chloride solution. If stored for a period of time, it is more beneficial to use the volatile components to self-evaporate and oxidize. However, the storage time should not be too long, so as to prevent the wood chips from decaying and deteriorating. When producing other activated carbon varieties, mixed wood chips of various tree species can be used. The requirements for wood chips are: particle size 6-40 mesh, without plate skin, wood block, sediment and iron filings, etc., the water content is 15%-20%.
In order to stabilize the process operation, the wood chips need to be screened with a vibrating screen, and the wood chips that meet the requirements are selected and impurities are removed to avoid affecting the product quality.
The selected wood chips have a moisture content of about 40%. Drying is generally carried out using a gas flow dryer. It consists of a hot blast stove, a fan and a drying tube. The drying tube is made of steel plate with a diameter of 300 mm and a height of about 20 m. The wood chips are sent to the drying pipe, and the hot air of 120-150 degrees Celsius sent by the hot air furnace drives the wood chips to pass through the drying pipe at a speed of 8 meters per second. The moisture content of the dried wood chips is reduced to 15%-20%, and separated by cyclone. Recycling.
The wood chips are dried, and some factories use rotary kiln. Wood chips are indirectly heated by the flue gas and dried. During production, the wood chips enter the cylinder body from one end of the feeding port, and slowly move forward with the rotation of the cylinder body and a certain slope, and the dried wood chips are continuously discharged from the discharging port. The flue gas generated by the combustion of the combustor first flows through the outside of the cylinder, heats the cylinder, and then enters the tobacco pipe inside the cylinder to fully exchange heat and finally discharge into the chimney. When operating, the amount of feed should be controlled according to the furnace temperature. At the same time, the furnace temperature should not be too high to prevent wood chips from burning.
Preparation of zinc chloride solution
The concentration of the zinc chloride solution varies depending on the type of activated carbon produced. The preparation of the zinc chloride solution refers to a zinc chloride solution formulated to a predetermined concentration, which is an important factor in ensuring the zinc-to-chip ratio. Industrial zinc chloride which is white, easy to absorb and deliquesce, and has a content of more than 96% should be used.
Due to the different uses of activated carbon, the requirements for using zinc chloride to make carbon are different, as follows:
The formulation requirements for activated carbon for sugar are:
The zinc chloride solution has a concentration of 50-57 Baume at 60 degrees Celsius and a pH of 3.0-3.5.
The formulation requirements for medicinal activated carbon are:
The zinc chloride solution has a concentration of 45-47 Baume at 60 degrees Celsius and a pH of 1.0-1.5.
In the preparation, in the zinc bath, the solid zinc chloride is dissolved in the zinc chloride solution recovered in the recovery process. If the recovered zinc solution is not enough, it can also be prepared with water. When the required Baume degree is reached, the pH of the solution is adjusted with hydrochloric acid.
Baume concentration is a widely used means of indicating the concentration of a solution in a zinc chloride process plant. The concentration measured by the Baume pycnometer immersed in the solution indicates the concentration.
The concentration of Baume in zinc chloride solution has a certain relationship with temperature. When the percentage concentration is constant, the concentration of Baume decreases with the increase of temperature. Therefore, for the Baume concentration of the zinc chloride solution, the temperature of the solution must be indicated. For example, to prepare a zinc chloride solution with a concentration of 45-46 Baume at 60 degrees Celsius, if it is at 30 degrees Celsius, it should be formulated with a concentration of 46-47 Baume.
The concentration of Bomei chloride solution (0Be?FONTFONT-SIZE: 14pt;">宋体" LANG="ZH-CN">) and temperature (degrees Celsius), the concentration and relative density of zinc chloride solution The relationship between the percent concentration can be found in the relevant chart.
Purpose and process conditions of the kneading process
The purpose of the kneading process is to continuously stir the wood chips and the zinc chloride solution by means of a pair of zigzag stirring blades in the kneader, repeatedly pressurizing them to uniformly mix them, and accelerate the penetration of the zinc chloride solution into the wood chips.
Kneading is carried out in a kneader. The kneading machine is made of acid-resistant steel, which is a horizontal semi-circular groove. The groove has a pair of zigzag agitators. The volume is generally 0.5 cubic meters, and the operation is intermittent. The kneading machine is provided with a transmission mechanism, and pressing the button of the mechanism enables the kneading machine to rotate the semicircular groove by an angle to pour the zinc scrap into the hopper of the rotary kiln.
For ease of operation, the kneading process also sets up a wood chip metering device and a zinc chloride solution high level tank and metering device. The wood chip metering device consists of a bucket elevator, scale and hopper that transports wood chips, which accurately controls the weight of each pinch and wood chip. A tube is connected to the upper part of the kneader in the lower part of the zinc chloride solution to uniformly spray the quantitative zinc chloride solution into the kneader and mix with the wood chips.
When kneading, the ratio of the weight of the process wood chips to the weight of the zinc chloride solution is called the ratio of the material to the liquid, sometimes referred to as the impregnation ratio.
The process conditions for kneading are:
1. Production of industrial activated carbon
Wood chip moisture content (%) 15-20
Concentration of zinc chloride solution at 60 degrees Celsius (Pomez) 45-47
Zinc chloride solution pH 1-1.5
Material to liquid ratio 1:3
Kneading time (minutes) 10-15
2. Production of activated carbon for sugar
Wood chip moisture content (%) 15-20
Concentration of zinc chloride solution at 60 degrees Celsius (Pomez) 50-57
Zinc chloride solution pH 3 - 3.5
Material to liquid ratio 1:4-5
Kneading time (minutes) 10-15
How does the rotary furnace operate? What are the process conditions for carbonization and activation?
Rotary furnace is a key equipment for carbonization and activation of zinc scrap. The rotary kiln is horizontal, with an inner diameter of 1 meter and a length of 13 meters. The cylinder is made of steel plate and lined with refractory bricks. A large gear is mounted on the outside of the middle of the cylinder to push the cylinder to rotate. There are a pair of rollers at each end to support the weight of the cylinder. There are seals on the burner and the furnace. The installation has an inclination of 2-4 degrees.
The rotary kiln is operated continuously, and the zinc scrap is fed into the furnace tail by a disc feeder and a screw feeder. The material moves slowly to the burner by the rotation and inclination of the cylinder. A combustion chamber is arranged in the burner to burn crude oil or gas, and the generated high-temperature flue gas directly enters the furnace, flows from the burner head to the furnace tail, and is in direct contact with the material countercurrent. In the carbonization process, a viscous plastic material is formed, adhered to the furnace wall, and agglomerated into a crucible to block the furnace. In order to prevent clogging, a chain-shaped star-shaped scraper is installed in the furnace, so that it will continuously hit the furnace wall as the cylinder rotates, and the agglomerated material stuck on the furnace wall is scraped off.
The activated material is called the activated material, which falls from the burner into the discharge chamber and is periodically taken out and sent to the recycling process. Waste flue gas enters the exhaust gas recovery system from the end of the furnace through the flue.
When the furnace is started, the converter is started first, and then the temperature is raised by the ignition. When the temperature of the furnace tail rises to about 300 degrees Celsius, the feeding is started. If it is necessary to stop the furnace, first stop the feeding, continue to maintain a certain furnace temperature, and wait until the materials in the furnace are completely discharged, and then stop the furnace. Before the furnace is not completely cooled, the cylinder is rotated once every few minutes to 20 minutes to prevent deformation of the cylinder.
The process conditions for carbonization and activation of rotary kiln are as follows:
Activation zone material temperature (degrees Celsius) 500-600
Charring, activation time (minutes) about 40
Furnace filling coefficient (%) 15-20
Cylinder speed (rev / min) 1-3
The pressure in the furnace is slightly negative
Furnace flue gas temperature (degrees Celsius) 700-800
Furnace flue gas temperature (degrees Celsius) 200-300
Discharge interval (minutes) 20
The purpose of the process of producing activated carbon by zinc chloride method
The activated material contains 70% to 90% zinc chloride and a zinc-containing compound. The purpose of recycling is to recover this part of zinc chloride and zinc-containing compounds, reducing the consumption of zinc chloride in the production of activated carbon, in order to reduce the cost of the product.
The recovery operation of zinc chloride belongs to the extraction method, that is, zinc chloride solution (zinc water for short) and a small amount of industrial hydrochloric acid are added to the activated material to dissolve zinc chloride and zinc oxide, and then separated by filtration.
The recycling is carried out in a recycling bin. The recycling bin is made of steel plate and is a cylindrical body. The inside and outside of the barrel are painted with diabase clay. A diabase plate is lined on the inside of the barrel. The lower part of the barrel is made of steel and diabase powder cast filter plates.
In operation, the activated material is added to the recovery tank, firstly added with the higher concentration of recovered zinc water to the activated material, and about 5% by weight of hydrochloric acid is added to convert the zinc oxide formed during activation into zinc chloride.
Stir well during the reaction. After the reaction is completed, let it stand for a few minutes, open the vacuum suction valve, draw the zinc chloride solution in the recovery tank into the vacuum drum, and then put it into the acid-resistant cylinder. Generally, the concentration of the zinc chloride solution recovered for the first time can reach 40 or more, and can be sent to prepare a zinc chloride solution. After the first recovery, the low-concentration zinc water is pumped into the recovery tank in turn, so that the zinc water covers the carbon surface, so that the recovery is repeated several times, and the recovered zinc water with different concentration is obtained, and respectively placed in the acid-resistant cylinder. Medium, for the next recycling. Until the various concentrations of zinc water left last time are used up, they are washed with hot water, and the washing liquid is also collected in the acid-resistant cylinder. Until the zinc chloride content in the char is less than 1%.
Activated carbon gas activation
Activated carbon gas activation method is a method of activating carbon dioxide, carbon dioxide, air, flue gas, etc. at 600 to 1 200 ° C after carbonization of the raw material. The main process is carbonization and activation, and carbonization is to heat the raw materials. The volatile component is removed to prepare a carbonized material suitable for the next activation. The carbonization process is divided into a primary decomposition reaction below 400 ° C, an oxygen bond cleavage reaction at 400 to 700 ° C, and a deoxygenation reaction at 700 to 1 000 ° C. In the reaction stage, the raw material, whether it is a chain molecular substance or an aromatic molecular substance, obtains a carbonized product of a three-dimensional network structure by condensing a planar molecule of a benzene ring through the above three reaction stages. The charcoal has low adsorption capacity due to the fact that the carbon contains a part of hydrocarbons, the pore volume is small, and the pores are blocked. The activation stage usually exposes the carbon to the oxidizing gas medium at about 900 °C. The first stage of activation is carried out by treatment, the adsorbed substance is removed and the blocked pores are opened; further activation is performed to enlarge the original pores and passages; and subsequently, the selection of the portion having high reactivity of the carbonaceous structure is selected. Sexual oxidation to form microporous tissue.
Activated carbon by microwave heating
The carbonaceous raw material is preheated at a temperature of 600 ° C or higher, and is contacted with water vapor, carbon dioxide, an oxygen-containing gas or a gas generated by activation, and is directly heated by microwave to complete the activation. However, activated carbon can be obtained by a usual activation method. It is impossible to use microwaves to heat up to the full activation temperature of coal, petroleum, wood, etc. For example, coal, asphalt, wood and other raw materials, if irradiated with microwaves, initially heat due to moisture, the temperature can reach about 100 °C. Then, when the water is evaporated, the heat is extremely small, and it is necessary to heat up to 100 ° C or more, or it may not be possible or take a long time.
Activated carbon microwave heating steam activation
The microwave heating steam activation method can significantly expand the internal surface area of ​​activated carbon. The specific process is as follows: firstly, the raw material is made into a certain particle size and specific gravity, and the water vapor is fully stirred to uniformly wet it. According to the capillary phenomenon, the fibers of the plant cellulose raw material are interposed. There is free water in the micropores, so that the raw materials are wet and swelled. Then, with these free waters as electrolytes, the microwaves are radiated, and the free water evaporates rapidly, generating vapor pressure, and explosively ejecting from the inside of the raw materials. The space between the fibers is enlarged, and at the same time, the space is sharply dried, and numerous cracks are generated. The porous structure of the raw material is more remarkable, and the internal surface area is further enlarged. Further, the carbonization is continuously performed, and steam is continuously supplied, and the steam continuously flows to the porous material and the raw material. The cracked place suppresses and eliminates the fixation of hydrocarbons until the carbonization is completed, and the porous structure is well maintained.
Use of drug activation and gas activation
Gas activation and drug activation are sometimes used together. The activated carbon activated by the drug is further activated by steam, and sometimes a product with a special pore distribution can be produced, and the number of pores having a wide range is increased. Treatment with activated carbon When a gas containing a substance that blocks pores of carbon is contained, for example, when benzene is adsorbed and removed from city gas by granular activated carbon, the pores of the activated carbon are clogged by diolefins in city gas and rapidly deteriorated. The activated carbon that can be used has been used in this type of activation method. The Benzier brand activated carbon of Leji Company is a representative of such activated carbon.
Continuous carbonization activation
The carbonization and the oxidation-activated activated carbon production method are continuously carried out in a relatively simple flow heating furnace, and the operation is labor-saving and the product quality is good. The method is characterized in that the water content is adjusted to 15% to 30% of the activated carbon raw material continuously. It is sent to the flow heating furnace, and an appropriate amount of air is blown from the bottom of the furnace to carbonize the furnace and restrict oxidation activation. When the raw material is put into the furnace and is loaded into the furnace, only a small amount of fire is sent into the furnace, and the furnace is added. The lower part of the drum is filled with an appropriate amount of air to promote partial combustion of the raw material to heat the raw material itself. The temperature inside the furnace and the rate of carbonization are adjusted by the amount of air blown and the amount of feed. The blast is used for partial combustion and heating of the raw material, and is also used for Particle fluidization during carbonization and continuous activation reactions.
One-step fluidized bed for the production of activated carbon
The fluidized bed one-step process for the production of activated carbon is a new process of coal-based activated carbon developed in recent years. The method directly screens the raw material into the fluidized bed, carbonizes and activates at the initial fluidization rate, and the activation temperature and the activation gas are evenly distributed. It can effectively activate the reaction raw materials. It can process both powdery raw materials and granular raw materials. The production process is simple and has been highly valued. The British National Coal Bureau has adopted this method to produce anthracite activated carbon which has been put into commercial operation. However, single-stage fluidization The bed is generally suitable for batch operation, and the continuous operation is not uniform. The Tasaki Mi 4 study shows that the increase in the number of fluidized bed sections allows the continuous activation and intermittent operation to receive the same activated product. However, the process produces severe wear and tear when forming activated carbon, such as Mixing the fine particles of pulverized coal with the molding raw materials, the wear can be greatly reduced, and the powdered and granular activated carbon can be prepared at the same time. The process is simpler than adding inert fine particles, and the equipment production capacity is also large.
Rapid carbonization activation
The researchers believe that the rapid pyrolysis process can produce cheap activated carbon, which has good adsorption performance and can be directly used as a gasification raw material without regeneration after use. The results of experimental research show that rapid pyrolysis can be significant. Increasing the specific surface area of ​​activated carbon and introducing high-temperature steam medium in the rapid pyrolysis process have a significant effect on the surface structure of activated carbon. Qiu Jieshan et al. used a falling bed radiant furnace to use potassium carbonate as a catalyst to investigate the catalysis of lignite in Huangxian County in water vapor medium. The possibility of rapid carbonization to produce activated carbon. The results show that the void structure index and adsorption performance index of the activated carbon obtained in the experiment have reached or approached the level of some commercially available activated carbon.
Lignite semi-coke briquetting activation process
At present, the application of lignite-made activated carbon is more common in the activation process of lignite semi-coke briquetting. This process firstly browns the coal, then pulverizes the semi-coke to less than 0.1 mm, adds the asphalt binder to form the compact, and pulverizes the compact and then activates it. Furnace activation, sieving or grinding to produce granular or powdered activated carbon. This process is used in Australia and Europe.
Other production methods of activated carbon
Zhang Shuangquan et al. explored a new process for the preparation of coal-based activated carbon based on nitrate-based oxidative composite catalyst. The catalyst was used to catalyze and oxidize. The results showed that cerium nitrate has poor activity and should not be used as a catalyst. Potassium compounds are A good catalyst for the production of activated carbon; the promoter phosphorus plays an important role in the development of the void structure of the activated carbon; the ash in the raw material hinders the performance of the catalyst; the experimental composite catalyst can increase the activation reaction rate by more than l times, in the same burning Obtain higher adsorption performance at the rate of loss, or increase the activation yield at the same rate of burnout, thereby reducing the production cost of activated carbon. Australia Robert will make 20% potassium hydroxide solution 70-75 ml with dry raw coal or pickled coal 20 g mixed into a gel paste, using a compression molding machine to press a coal section with a diameter of 6 mm. After drying, the diameter becomes 3 mm, hard, and then distilled under nitrogen protection at 900 ° C for 16 h. The carbonized charcoal is extracted with dilute acid to recover potassium. The product is obtained after salt. The surface area of ​​raw coal activated carbon is l 340 m / g, and the acid washed coal is l 500 square meters / g. A similar process is also developed in the United States, but hydrogen and oxygen The potassium dosage is larger, and the surface area of ​​the powdered activated carbon is up to 3,000 square meters/g. However, in the United States, the raw brown coal and the sub-bituminous coal are treated with dilute acid (such as phosphoric acid). The purpose of the treatment is not to leach the mineral, but to make the coal Some components are cross-linked, and then activated by direct briquetting to produce activated carbon, the yield and activity are greatly improved.
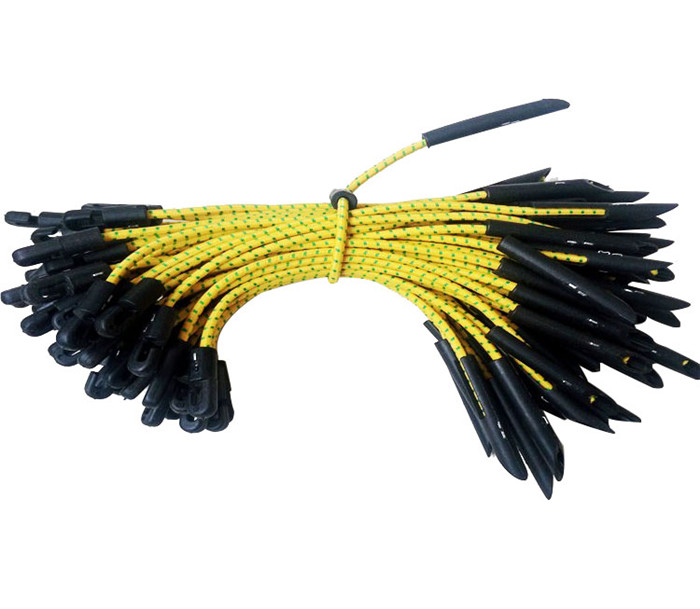
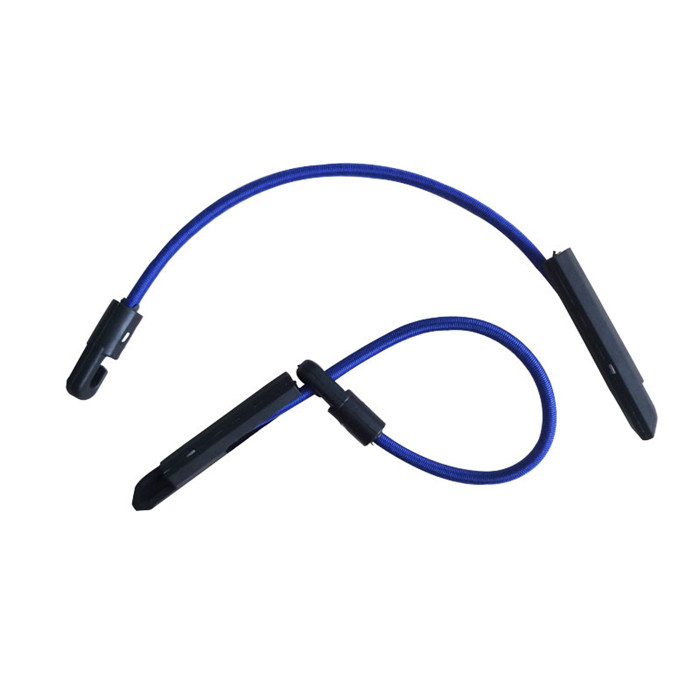
Elastic Tie is also called Elastic Tie for Scaffolding Sheets, fixing strips, toggle tie , bungee tie ,plastic Ball bungee cord,Elastic Shock Cord Ties, Scaffold Tie Downs Hook and Toggle Stretch Fix.
It is made of elastic rubber cord with hook and toggle. It is a kind of multi-purpose fastening item usually used in construction filed for fixing scaffolding sheets onto scaffold.
Elasticated Shock Cord Ties are most commonly used for fixing scaffold sheeting, but they can also be used to tie tarpaulins down. The total length of each shock cord is approximately 30cm, with a total stretch of approximately 40cm. Now featuring a handy rounded toggle which is easier to fit through tarpaulin eyelets.
Material :Inside latex thread & outside polyester
Length:300mm (12")
Diameter :5mm,5.2mm, 5.6mm
Cord Extension:75%
Breaking Load 630N
Package 100 pcs/bag, 10 bags/carton
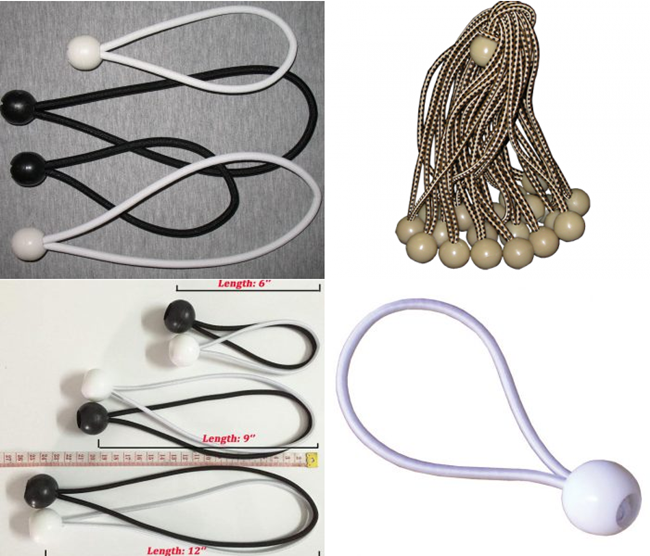



Elastic Tie
Elastic Tie,Elastic Tarp Strap Tie,Elastic Rope Tarp Tie,Rubber Tarp Tie
HEBEI OHONG PLASTIC CO. LTD. , http://www.tarpaulin-factory.com